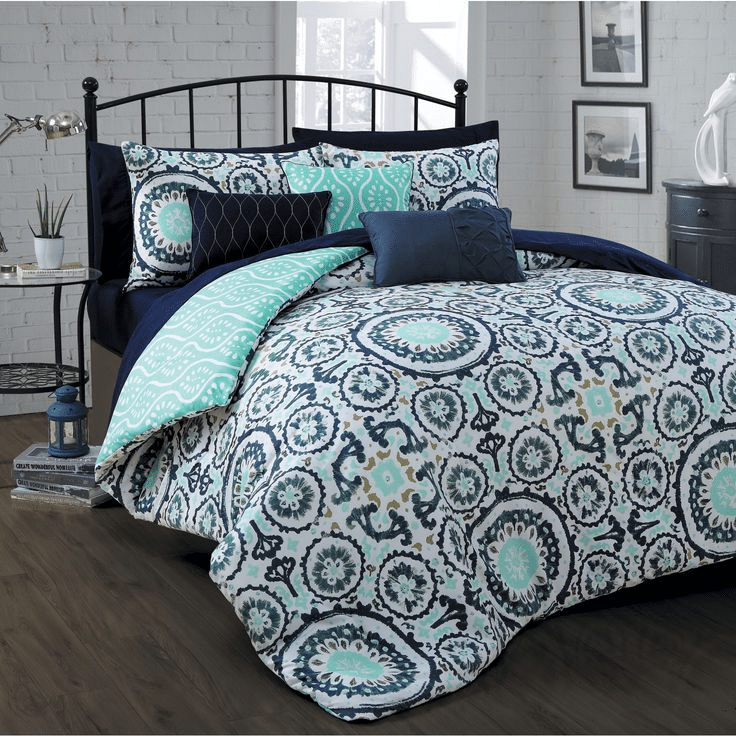
Pavement or road preservation is a significant consideration of managers and owners of parking lots, highways, streets and all kinds of roads or sidewalks. The reason for the concern is that pavements are deteriorating steadily because of weather time and traffic. These kinds of situations are a huge deal.
There are more or less four million miles of public roads and pavements in the United States that is valued close to $2 trillion. The sidewalks and streets in the United States are a considerable investment and crucial for moving goods and people systematically and methodically.
In order to understand and apply street preservation, we will take a closer look at the overview of this topic, including the explanation of what maintenance of pavement is all about a short description of the types of treatments, as well as information on the available resources to people who are interested in additional details. For more information about California, New York or asphalt maintenance janesville wi tips (or state asphalt in general), you can visit websites, social media or forum sites about this topic.
Pavement preservation, what is it?
A simple definition of street preservation could be doing improvement or maintenance and taking care of existing road assets. A lot of people have probably heard the phrase ” Right care on the right road at the right time.” But preserving the street has reached a level of acceptance, there are words that are included in the federal legislation that will provide a better definition of the term.
Public Law 112-141, “MAP-21 or the Moving Ahead for Progress in the 21st Century Act,” say that the term Pavement Preservation Activities and Programs means activities and programs engaging a long-term and network-level strategy that helps enhance the street performances by using a cost-effective and integrated set of practices that extend the life of the pavement, meet all the user expectations, as well as improve the overall safety of the road or sidewalk.
The National Center for Pavement Preservation or NCPP defines the preservation of pavement the same way. Still, it replaces the vague phrase “meets all the user expectations” with the words “improves the motorist satisfaction at the same time save public tax money.” So, street or road preservation is applying part of tax payer’s money to preserve existing roads and sidewalks by using a proven method in a timely manner. These methods include:
Crack filling and crack sealing
Asphalt rejuvenators and fog seals
Seal treatments like sand, scrub, cape and chip
Micro-surfacing and slurry seal
Overlays like the ultra-thin bonded wearing course and thin
Visit https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moving_Ahead_for_Progress_in_the_21st_Century_Act for more information about MAP-21.
Crack filling and sealing
There are two known approaches to address cracks – filling and sealing. Crack sealing is a more permanent and involved approach between the two. It is intended to help prevent foreign materials and water from entering the cracks on the road and pavement.
Sealing the crack is needed when there’s a movement of the way at the crack, usually referred to as working cracks. The filling will require little prep work and they are intended to minimize the amount of water that is entering the street. Both can help extend the life of the road by minimizing raveling, fatigue and stripping.
Asphalt rejuvenator and fog seal
Fog seals are light applications of diluted slow-setting asphalt emulsions that are sprayed on the existing surface. It is usually used in renewing HMA pavements that started to become brittle because of age, address surface defects and small cracks, as well as lessen the raveling. The rejuvenating emulsion can be put as a seal to help improve the properties of the aged asphalt by substituting some asphalt components or maltenes that are lost during the aging process.
Click here for more information about chip sealing.
Seal treatment
Scrub and sand seals are sprayed administration of asphalt emulsion followed by the covering of fine chips and sand. Scrub seals use a squeegee or a broom to force emulsions to the cracks before road aggregate is used. If rolling is finished, rubber tire rollers will be used.
These types of sealing operations use the same tools and equipment as chip sealing, with brooming mechanisms added to them to scrub sealing. Sans seal usually adds three or four years of road life and seals can add four to six years of extra service.
Micro-surfing and slurry seals
Slurry seal is a mixture of mineral fillers, fine aggregate, water and asphalt emulsions. They are being used as surface treatment and it is usually the thickness if the biggest aggregate particle. They are now expanding the structural capacity of the pavement. Still, it can help minimize the surface distress that is caused by seal non-working road cracks, oxidation, improve resistance to skids and end raveling.